ΝΑΥΤΙΚΑ ΗΛΕΚΤΡΟΝΙΚΑ ΟΡΓΑΝΑ
ΥΠΕΡΒΟΛΙΚΗ ΝΑΥΤΙΛΙΑ
LORAN C
eLORAN
By Capt. Nikolaos I. Skouloudis
PGDip in Business Administration
Πίνακας περιεχομένων
2. Γενικές αρχές υπερβολικής ναυτιλίας
3. Χαρακτηριστικά και λειτουργία του συστήματος LORAN-C
4. Σφάλματα του συστήματος LORAN-C
5. Εφαρμογές του συστήματος LORAN-C στην ναυτιλία και άλλες βιομηχανίες
Ø Επιστημονική Έρευνα και Γεωργία
Ø Άλλες Βιομηχανικές Εφαρμογές
6. Ιστορική εξέλιξη και εφαρμογές
6.1. Αναβάθμιση και ενοποίηση με GPS και άλλες τεχνολογίες
6.2. Αντοχή στις Παρεμβολές και Διαταραχές
6.3. Μακροπρόθεσμη Βιωσιμότητα και Κόστος
6.4. Μέλλον του eLORAN και Συνεχιζόμενη Ανάπτυξη
6.5. Επιπτώσεις του eLORAN στην Ασφάλεια της Ναυσιπλοΐας
6.6. Κανονιστικές Προεκτάσεις και Υιοθέτηση από Διεθνείς Οργανισμούς
6.7. Ανάγκη για Εκπαίδευση και Υποστήριξη
6.9. Προκλήσεις και Μελλοντικές Προοπτικές του eLORAN
6.10. Πολιτική Υποστήριξη και Διεθνής Συνεργασία
6.11. Συνοψίζοντας τις Ανάγκες του Μέλλοντος
6.12. Η Συμβολή της Τεχνολογίας στο Μέλλον της Ναυτιλίας
6.13. Ανάγκες για Εκπαίδευση και Κατάρτιση
6.14. Υποστήριξη και Συντήρηση Υποδομών
Ανάλυση Φωτογραφίας 1: Διάγραμμα Υπερβολικών Καμπυλών
Ανάλυση Φωτογραφίας 2: Συσκευή Δέκτη LORAN-C
1. Εισαγωγή
Τα ναυτικά ηλεκτρονικά όργανα έχουν γίνει αναπόσπαστο μέρος του σύγχρονου ναυτικού εξοπλισμού, παρέχοντας στους ναυτιλλόμενους τα απαραίτητα εργαλεία για ασφαλή και αποτελεσματική πλοήγηση. Η ναυσιπλοΐα απαιτεί ακριβείς μετρήσεις θέσης, πορείας και ταχύτητας, ειδικά σε ανοιχτές θάλασσες ή σε περιοχές όπου η δορυφορική κάλυψη μπορεί να είναι περιορισμένη ή ανύπαρκτη. Το LORAN-C και άλλα συστήματα υπερβολικής ναυτιλίας, βασισμένα σε γεωμετρικές αρχές, έχουν κεντρικό ρόλο στην εξασφάλιση αυτών των δεδομένων, καλύπτοντας τις ανάγκες πλοηγών και πληρωμάτων που εργάζονται σε θαλάσσιες περιοχές ή ακόμη και σε παραθαλάσσιες ζώνες με δυσχερείς συνθήκες.
Η σύγχρονη ναυσιπλοΐα εξελίσσεται συνεχώς χάρη στις τεχνολογικές καινοτομίες, με το GPS να κυριαρχεί στην παγκόσμια ναυτιλία. Ωστόσο, το σύστημα LORAN-C παραμένει πολύτιμο εργαλείο σε περιοχές που δεν καλύπτονται επαρκώς από δορυφορικές υπηρεσίες ή όπου οι δορυφορικές παρεμβολές μπορούν να επηρεάσουν την ακριβή πλοήγηση. Η αξία του LORAN-C έγκειται στην ικανότητά του να προσφέρει ακρίβεια και αξιοπιστία ακόμα και σε απομακρυσμένες περιοχές, κάνοντάς το έναν ουσιαστικό σύμμαχο για ναυτικούς και επαγγελματίες της ναυτιλίας.
Αυτό το εγχειρίδιο στοχεύει να προσφέρει μια πλήρη ανασκόπηση των βασικών αρχών και χαρακτηριστικών των ναυτικών ηλεκτρονικών οργάνων, με έμφαση στο σύστημα LORAN-C, αλλά και άλλα συναφή συστήματα. Στοχεύει να καλύψει τις ανάγκες των μαθητών των Ναυτικών Ακαδημιών και των επαγγελματιών του ναυτιλιακού τομέα, με στόχο να προσφέρει μια ουσιαστική κατανόηση των θεωρητικών και πρακτικών πτυχών αυτών των συστημάτων.
Η ναυσιπλοΐα, ως επιστήμη και τέχνη, βασίζεται σε συστήματα και εργαλεία που επιτρέπουν την ακριβή καθοδήγηση των πλοίων και τη διαχείριση των κινδύνων που προκύπτουν κατά τη διάρκεια του ταξιδιού. Στην καρδιά αυτής της διαδικασίας βρίσκονται τα ναυτικά ηλεκτρονικά όργανα, τα οποία συνδυάζουν τη γεωμετρία με προηγμένες τεχνολογίες για τον εντοπισμό και την παρακολούθηση της θέσης του πλοίου.
Το LORAN-C, ως ένα από τα πιο δημοφιλή και ευρέως χρησιμοποιούμενα συστήματα υπερβολικής ναυτιλίας, βασίζεται στην εκπομπή ραδιοσημάτων από έναν κεντρικό σταθμό και διάφορους δευτερεύοντες σταθμούς. Η τεχνολογία του επιτρέπει την ακριβή καθοδήγηση πλοίων ακόμη και σε περιοχές που δεν καλύπτονται από δορυφορικά συστήματα πλοήγησης, προσφέροντας αξιόπιστες και ακριβείς μετρήσεις για τον καθορισμό της θέσης, της πορείας και της ταχύτητας του πλοίου. Ουσιαστικά, το LORAN-C παρέχει μία εναλλακτική λύση στον τομέα της ναυσιπλοΐας, καλύπτοντας περιοχές που συχνά αντιμετωπίζουν δυσκολίες με το GPS ή άλλα σύγχρονα συστήματα πλοήγησης.
Τα ναυτικά ηλεκτρονικά όργανα όπως το LORAN-C χρησιμοποιούνται σε ποικιλία εφαρμογών, από τη βασική πλοήγηση και την ασφάλεια στον θαλάσσιο χώρο μέχρι πιο εξειδικευμένες εφαρμογές όπως η διαχείριση του φορτίου και η προσέγγιση λιμένων. Η τεχνολογία πίσω από αυτά τα συστήματα είναι τόσο ευέλικτη ώστε να μπορεί να υποστηρίξει τις ανάγκες διαφορετικών τύπων πλοίων, από μικρά εμπορικά σκάφη μέχρι μεγάλα επιβατηγά ή στρατιωτικά πλοία.
Η αξία αυτών των ναυτικών ηλεκτρονικών οργάνων δεν περιορίζεται μόνο στην ακρίβεια και τη λειτουργικότητά τους. Σημαντική είναι και η συμβολή τους στην αύξηση της ασφάλειας των πληρωμάτων και των πλοίων. Η πλοήγηση σε ανοικτές θάλασσες, σε περιοχές με δύσκολες καιρικές συνθήκες, ή η προσέγγιση σε λιμάνια με περιορισμένη ορατότητα, απαιτούν αξιόπιστα και ακριβή εργαλεία για τη μείωση των κινδύνων και την αποφυγή ατυχημάτων. Τα ναυτικά ηλεκτρονικά όργανα παρέχουν αυτήν ακριβώς την ασφάλεια, παρέχοντας στους ναυτιλλόμενους τα δεδομένα που χρειάζονται για να κάνουν τις σωστές αποφάσεις.
Ο σκοπός αυτού του εγχειριδίου είναι να προσφέρει στους αναγνώστες μια κατανόηση των θεμελιωδών αρχών που διέπουν τα ναυτικά ηλεκτρονικά όργανα, συμπεριλαμβανομένων των βασικών αρχών του LORAN-C και της λειτουργίας του. Επιπλέον, το εγχειρίδιο παρέχει και αναλυτική παρουσίαση των πιο σημαντικών εφαρμογών αυτών των συστημάτων, καθώς και των δυνατοτήτων που προσφέρουν στην καθημερινή ναυσιπλοΐα.
Η σύνδεση της θεωρίας με την πρακτική είναι απαραίτητη για την πλήρη κατανόηση της αξίας των ναυτικών ηλεκτρονικών οργάνων, γι' αυτό και το εγχειρίδιο περιλαμβάνει πλήθος ερωτήσεων και απαντήσεων που καλύπτουν όλες τις πτυχές του LORAN-C και των συναφών συστημάτων. Με τον τρόπο αυτό, το εγχειρίδιο λειτουργεί ως εκπαιδευτικό εργαλείο για την εμβάθυνση στην επιστήμη της ναυσιπλοΐας και της ναυτικής τεχνολογίας, βοηθώντας τους αναγνώστες να κατανοήσουν τα συστήματα που χρησιμοποιούνται για την ασφάλεια και την αποδοτικότητα της σύγχρονης ναυτιλίας.
2. Γενικές αρχές υπερβολικής ναυτιλίας
Η υπερβολική ναυτιλία αποτελεί έναν από τους πιο βασικούς και αξιόπιστους τρόπους προσδιορισμού της θέσης ενός πλοίου ή αεροσκάφους, βασιζόμενη σε γεωμετρικές αρχές και τη χρήση ραδιοσημάτων. Η τεχνική αυτή επιτρέπει την ακριβή τοποθέτηση ενός σκάφους χωρίς την ανάγκη από δορυφορικές πηγές, όπως το GPS. Η βασική αρχή της υπερβολικής ναυτιλίας είναι η εκμετάλλευση της διαφοράς χρόνου άφιξης (Time Difference of Arrival, TDOA) μεταξύ σημάτων που εκπέμπονται από δύο ή περισσότερους σταθμούς εκπομπής. Κάθε σταθμός εκπέμπει σήματα που διαδίδονται μέσω του αέρα και άλλων μέσων, όπως η θάλασσα ή η ξηρά, και η διαφορά στον χρόνο άφιξης αυτών των σημάτων στα διάφορα σημεία του σκάφους επιτρέπει την υπολογιστική προσδιορισμό της θέσης του σκάφους μέσω των υπερβολικών γραμμών θέσης. Αυτές οι υπερβολικές γραμμές είναι γεωμετρικές καμπύλες που τοποθετούν το σκάφος σε συγκεκριμένες θέσεις στο γεωγραφικό χώρο.
Η αλυσίδα των σταθμών εκπομπής παίζει σημαντικό ρόλο στην ακριβή πλοήγηση με υπερβολική ναυτιλία. Στην περίπτωση της ναυτιλίας, κάθε αλυσίδα περιλαμβάνει έναν κύριο σταθμό (master station) και αρκετούς δευτερεύοντες σταθμούς (secondary stations), οι οποίοι επικοινωνούν μεταξύ τους και με το σκάφος. Η ακρίβεια του συστήματος επηρεάζεται από διάφορους παράγοντες, όπως η γεωμετρία των σταθμών εκπομπής, η ισχύς του σήματος και η ποιότητα των δεκτών σήματος. Οι σταθμοί πρέπει να είναι τοποθετημένοι με τρόπο που να επιτρέπει τη μέγιστη ακρίβεια στην υπολογιστική ανίχνευση της θέσης του σκάφους.
Η υπερβολική ναυτιλία προσφέρει πολλά πλεονεκτήματα σε σχέση με άλλες τεχνικές πλοήγησης. Ένα από τα σημαντικότερα πλεονεκτήματα είναι η ανθεκτικότητα του συστήματος στις καιρικές συνθήκες και τις παρεμβολές από εξωτερικούς παράγοντες, όπως οι ηλεκτρομαγνητικές διαταραχές. Αυτό καθιστά την υπερβολική ναυτιλία ιδανική για χρήση στην ανοιχτή θάλασσα, όπου οι καιρικές συνθήκες και η έλλειψη άλλων πηγών σήματος μπορούν να επηρεάσουν αρνητικά άλλες μεθόδους πλοήγησης. Η υπερβολική ναυτιλία προσφέρει επίσης αξιοπιστία και ακριβή εντοπισμό θέσης σε περιοχές όπου η δορυφορική κάλυψη είναι περιορισμένη ή ανύπαρκτη. Ειδικότερα, σε περιοχές εκτός του εύρους κάλυψης του GPS, το σύστημα αυτό συνεχίζει να προσφέρει αξιόπιστη πλοήγηση. Ωστόσο, η απόδοση της υπερβολικής ναυτιλίας εξαρτάται από τον σωστό συγχρονισμό των σταθμών εκπομπής και την ικανότητα του συστήματος να διορθώνει τα σφάλματα που προκύπτουν από τη διάδοση των ραδιοκυμάτων μέσω διαφορετικών μέσων. Αυτό απαιτεί εξειδικευμένα εργαλεία και συσκευές που να διασφαλίζουν την ποιότητα του σήματος και την ακρίβεια του υπολογισμού της θέσης.
3. Χαρακτηριστικά και λειτουργία του συστήματος LORAN-C
Το LORAN-C (Long Range Navigation) αποτελεί ένα από τα πιο αξιόπιστα συστήματα υπερβολικής ναυτιλίας, που χρησιμοποιείται σε μεγάλες αποστάσεις και προσφέρει υψηλή ακρίβεια και αξιοπιστία στην πλοήγηση, τόσο για πλοία όσο και για αεροσκάφη. Το σύστημα βασίζεται στην εκπομπή ραδιοσημάτων από σταθμούς, οι οποίοι είναι οργανωμένοι σε αλυσίδες. Κάθε αλυσίδα περιλαμβάνει έναν κύριο σταθμό (master station) και αρκετούς δευτερεύοντες σταθμούς (secondary stations), οι οποίοι συνεργάζονται για την αποστολή σημάτων. Οι σταθμοί εκπέμπουν ραδιοσήματα σε προκαθορισμένα χρονικά διαστήματα, και οι δέκτες LORAN-C στα πλοία και τα αεροσκάφη μετρούν τη χρονική διαφορά άφιξης αυτών των σημάτων για να προσδιορίσουν τη θέση τους.
Η λειτουργία του LORAN-C βασίζεται στην ιδέα της μέτρησης της διαφοράς χρόνου άφιξης των σημάτων από διάφορους σταθμούς. Αυτές οι μετρήσεις επιτρέπουν τον υπολογισμό υπερβολικών γραμμών θέσης, οι οποίες ενώνουν τα σημεία με την ίδια χρονική διαφορά από τους σταθμούς. Η τομή αυτών των γραμμών καθορίζει την ακριβή θέση του σκάφους. Το LORAN-C είναι ιδιαίτερα χρήσιμο για την πλοήγηση σε περιοχές όπου η δορυφορική κάλυψη είναι περιορισμένη ή δεν υπάρχει καθόλου κάλυψη GPS, και η ακρίβειά του κυμαίνεται από 15 έως 500 μέτρα, ανάλογα με την απόσταση από τους σταθμούς εκπομπής. Ειδικότερα, σε αποστάσεις 200 ναυτικών μιλίων από τον κύριο σταθμό, η ακρίβεια μπορεί να είναι μεταξύ 15 και 90 μέτρων, ενώ σε αποστάσεις 1.000 ναυτικών μιλίων μπορεί να φτάσει τα 150 έως 500 μέτρα.
Το LORAN-C προσφέρει επίσης μεγάλο εύρος κάλυψης, με εμβέλεια έως και 1.080 ναυτικά μίλια, γεγονός που το καθιστά ιδανικό για πλοήγηση σε ανοιχτές θάλασσες. Η λειτουργία του παραμένει αξιόπιστη ακόμη και σε δύσκολες συνθήκες, όπως σε καταιγίδες ή σε περιοχές με ηλεκτρομαγνητικές παρεμβολές, κάτι που καθιστά το LORAN-C πολύ αποτελεσματικό στις συνθήκες αυτές. Οι σύγχρονοι δέκτες LORAN-C διαθέτουν τεχνολογίες επεξεργασίας σήματος που επιτρέπουν τη διόρθωση των σφαλμάτων που προκύπτουν από τη διάδοση των ραδιοκυμάτων σε διάφορα περιβάλλοντα, όπως η θάλασσα ή η ξηρά, διασφαλίζοντας την ακριβή πλοήγηση.
Ένα από τα βασικά χαρακτηριστικά του συστήματος LORAN-C είναι η ικανότητά του να ενσωματώνει διορθώσεις για τοπικά σφάλματα. Μέσω πινάκων και χαρτών που παρέχουν πληροφορίες για την περιοχή πλεύσης, οι δέκτες μπορούν να διορθώσουν την ακρίβεια του προσδιορισμού θέσης, μειώνοντας έτσι τα σφάλματα που προκαλούνται από περιβαλλοντικούς παράγοντες. Οι δέκτες του LORAN-C είναι επίσης εξοπλισμένοι με λειτουργίες που επιτρέπουν τον υπολογισμό της απόστασης και της πορείας προς συγκεκριμένα σημεία, διευκολύνοντας τον σχεδιασμό και την εκτέλεση των ναυτικών ταξιδιών.
Οι δέκτες LORAN-C επιτρέπουν στους ναυτιλλόμενους να σχεδιάζουν διαδρομές, να αποθηκεύουν σημεία ενδιαφέροντος (waypoints) και να υπολογίζουν την απόσταση και την διόπτευση προς τον επόμενο στόχο. Ένα άλλο χαρακτηριστικό του συστήματος είναι η δυνατότητα ενσωμάτωσης διορθώσεων για την ακρίβεια του στίγματος, έτσι ώστε να εξασφαλίζεται η υψηλή ποιότητα των δεδομένων και η ακριβής πλοήγηση ακόμα και σε περιοχές με περίπλοκες γεωγραφικές συνθήκες ή έντονα καιρικά φαινόμενα.
Αν και η χρήση του LORAN-C έχει μειωθεί με την έλευση των δορυφορικών συστημάτων πλοήγησης όπως το GPS, το σύστημα εξακολουθεί να χρησιμοποιείται ως εφεδρικό σύστημα πλοήγησης σε περιοχές όπου η δορυφορική κάλυψη είναι περιορισμένη ή ανύπαρκτη, καθώς και σε περιοχές που πλήττονται από ηλεκτρομαγνητικές παρεμβολές. Η αξία του LORAN-C παραμένει ιδιαίτερα σημαντική, δεδομένων των περιορισμένων δυνατοτήτων των άλλων συστημάτων σε ορισμένες γεωγραφικές περιοχές, και το σύστημα συνεχίζει να αποτελεί αξιόπιστο εργαλείο για την ναυτιλία.
4. Σφάλματα του συστήματος LORAN-C
Τα σφάλματα του συστήματος LORAN-C μπορούν να διακριθούν σε δύο βασικές κατηγορίες: τα συστηματικά σφάλματα και τα τυχαία σφάλματα. Τα συστηματικά σφάλματα προκαλούνται από προβλέψιμες φυσικές ή τεχνικές αιτίες και συνήθως οφείλονται στη διάδοση των σημάτων μέσω διαφορετικών περιβαλλόντων, όπως η θάλασσα, η ξηρά ή ο αέρας. Όταν τα σήματα διαδίδονται εν μέρει πάνω από θάλασσα και εν μέρει πάνω από ξηρά, δημιουργούνται καθυστερήσεις που αναφέρονται ως Additional Secondary Phase Factor (ASF). Αυτά τα συστηματικά σφάλματα μπορούν να διορθωθούν μέσω ειδικών πινάκων, χαρτών και ενσωματωμένων διορθώσεων στους δέκτες του συστήματος.
Τα τυχαία σφάλματα προκύπτουν από απρόβλεπτες αιτίες, όπως οι καιρικές συνθήκες, οι ηλεκτρομαγνητικές παρεμβολές από άλλες ραδιοσυχνότητες ή ακόμα και οι διαταραχές από φυσικά φαινόμενα, όπως οι καταιγίδες ή οι ηλιακές εκλάμψεις. Επειδή τα τυχαία σφάλματα δεν μπορούν να προβλεφθούν και να ελεγχθούν εκ των προτέρων, οι σύγχρονοι δέκτες του LORAN-C διαθέτουν μηχανισμούς για την ανίχνευση αυτών των σφαλμάτων και την ελαχιστοποίησή τους μέσω συστημάτων αντιστάθμισης και διόρθωσης.
Η γεωμετρία των σταθμών εκπομπής επηρεάζει επίσης την ακρίβεια του συστήματος, καθώς αν η γωνία μεταξύ του στίγματος του πλοίου και των σταθμών εκπομπής είναι πολύ μικρή ή πολύ μεγάλη, μπορεί να προκαλέσει αυτό που είναι γνωστό ως γεωμετρική αλλοίωση (Geometric Dilution of Precision - GDOP). Αυτή η αλλοίωση μειώνει την ακρίβεια του συστήματος, καθώς οι μικρές γωνίες μεταξύ των σταθμών εκπομπής και του πλοίου δημιουργούν αβεβαιότητα στη μέτρηση του στίγματος.
Για να ελαχιστοποιηθεί η επίδραση αυτών των σφαλμάτων, η σωστή επιλογή των σταθμών εκπομπής και η χρήση εξελιγμένων δεκτών είναι απαραίτητη. Επίσης, η τακτική συντήρηση των σταθμών εκπομπής και η εκπαίδευση των χειριστών για την κατανόηση των περιορισμών του συστήματος συμβάλλουν στη μείωση των σφαλμάτων και στη βελτίωση της ακρίβειας της ναυτιλίας.
Η κατανόηση των σφαλμάτων που ενδέχεται να προκύψουν κατά τη λειτουργία του LORAN-C είναι κρίσιμη για την αποτελεσματική χρήση του. Οι ναυτιλλόμενοι και οι χειριστές των συστημάτων πρέπει να είναι ενημερωμένοι για τις δυνατότητες και τους περιορισμούς του LORAN-C, ώστε να εξασφαλίζεται η ακριβής πλοήγηση και να αντιμετωπίζονται γρήγορα τυχόν προβλήματα που μπορεί να προκύψουν κατά τη χρήση του.
1. Συστηματικά είναι τα σφάλματα που δημιουργούνται σύμφωνα με ορισμένους φυσικούς ή μαθηματικούς νόμους με αποτέλεσμα να επιδρούν με τον ίδιο τρόπο σε όλες τις μετρήσεις. Τα σφάλματα αυτά είναι δυνατόν να επαλειφθούν με την εφαρμογή των αντίστοιχων διορθώσεων. Τέτοια είναι:
Ø Σφάλματα λόγω διαδόσεως των σημάτων Loran-C με ουράνιο κύμα
Ø Σφάλμα λόγω διαδόσεως των σημάτων Loran-C αποκλειστικά πάνω από θαλάσσια περιοχή.
Ø Σφάλμα λόγω διαδόσεως των σημάτων Loran-C πάνω από ξηρά
2. Τυχαία σφάλματα τα οποία οφείλονται σε αστάθμητους παράγοντες η δημιουργία τους δεν είναι τυχαία και δεν ακολουθεί κανένα κανόνα και για αυτό δεν είναι δυνατός ο υπολογισμός αντίστοιχων διορθώσεων. Παρ’ όλα αυτά οι σύγχρονοι δέκτες Loran-C έχουν την δυνατότητα να προειδοποιούν το ναυτιλλόμενο για την ύπαρξη τους έτσι ώστε να λάβει τα κατάλληλα μέτρα για να αποφύγει τις επιπτώσεις τους.
5. Εφαρμογές του συστήματος LORAN-C στην ναυτιλία και άλλες βιομηχανίες
Το LORAN-C, αν και παραδοσιακά συνδεδεμένο με τη ναυτιλία, έχει εφαρμογές σε διάφορους τομείς, παρέχοντας αξιόπιστη πλοήγηση και γεωεντοπισμό. Εκτός από τη χρήση του στη ναυτιλία, το σύστημα έχει επεκταθεί και σε άλλες βιομηχανίες που απαιτούν ακριβή και αξιόπιστα στίγματα σε μεγάλες αποστάσεις, όπως η αεροπορία, η επιστημονική έρευνα, και η γεωργία. Στη ναυτιλία, όμως, η κύρια εφαρμογή του LORAN-C παραμένει να παρέχει πλοήγηση σε περιοχές όπου οι δορυφορικές υπηρεσίες, όπως το GPS, ενδέχεται να μην είναι αξιόπιστες ή προσβάσιμες.
Ø Ναυτιλία
Η χρήση του LORAN-C στην ναυτιλία είναι θεμελιώδης για τις περιοχές του κόσμου όπου οι δορυφορικές υπηρεσίες δεν παρέχουν επαρκή κάλυψη ή είναι περιορισμένες λόγω γεωγραφικών συνθηκών. Το σύστημα παρέχει αξιόπιστη πλοήγηση σε ανοιχτές θάλασσες και στις θαλάσσιες περιοχές κοντά στις ακτές, βοηθώντας τα πλοία να εντοπίζουν τη θέση τους και να διασφαλίζουν τη σωστή κατεύθυνση. Στο παρελθόν, το LORAN-C ήταν το κύριο σύστημα πλοήγησης για τα πλοία, πριν την ευρεία υιοθέτηση των δορυφορικών συστημάτων. Ωστόσο, παραμένει σημαντικό ως εφεδρικό σύστημα για τη ναυτιλία, ειδικά σε περιπτώσεις όπου το GPS ενδέχεται να έχει παρεμβολές ή να είναι εκτός λειτουργίας.
Ø Αεροπορία
Η εφαρμογή του LORAN-C στην αεροπορία είναι λιγότερο διαδεδομένη από τη ναυτιλία, ωστόσο το σύστημα χρησιμοποιείται για πλοήγηση αεροσκαφών σε μεγάλες αποστάσεις, κυρίως σε περιοχές όπου η δορυφορική κάλυψη μπορεί να είναι περιορισμένη. Σε αυτές τις περιοχές, το LORAN-C χρησιμοποιείται για τη μέτρηση της απόστασης και τη διατήρηση μιας ασφαλούς πορείας πτήσης, με ιδιαίτερη έμφαση σε περιοχές της ατμόσφαιρας που είναι απομακρυσμένες ή σε περιοχές με πυκνές καταιγίδες και άλλες παρεμβολές.
Ø Επιστημονική Έρευνα και Γεωργία
Το LORAN-C χρησιμοποιείται επίσης σε επιστημονικές εφαρμογές και γεωργικές έρευνες, όπως στην παρακολούθηση του εδάφους και στη γεωαναγνώριση για την αποτύπωση της κίνησης του εδάφους ή άλλων φυσικών παραμέτρων. Στην γεωργία, μπορεί να χρησιμοποιηθεί για την παρακολούθηση καλλιεργειών και για την ακριβή τοποθέτηση εξοπλισμού και αρδευτικών συστημάτων σε εκτάσεις μεγάλων γεωργικών περιοχών.
Ø Άλλες Βιομηχανικές Εφαρμογές
Το LORAN-C έχει επίσης εφαρμογές σε βιομηχανίες που απαιτούν ακριβή γεωχωρική τοποθέτηση και παρακολούθηση σε μεγάλες αποστάσεις. Για παράδειγμα, χρησιμοποιείται στην ενέργεια για την παρακολούθηση υποδομών υπεράκτιων πλατφορμών πετρελαίου και φυσικού αερίου, καθώς και στην παρακολούθηση των έργων υποδομής και στις κατασκευές μεγάλης κλίμακας.
Αξιοσημείωτο είναι το γεγονός ότι, παρά την αύξηση των δορυφορικών συστημάτων πλοήγησης, το LORAN-C παραμένει ένα ισχυρό εργαλείο σε περιοχές με δύσκολες γεωγραφικές συνθήκες ή σε περιοχές όπου οι δορυφορικές υπηρεσίες μπορεί να υποφέρουν από παρεμβολές.
6. Ιστορική εξέλιξη και εφαρμογές
Η ανάπτυξη των ναυτικών συστημάτων υπερβολικής ναυτιλίας ξεκίνησε κατά τη διάρκεια του Β' Παγκοσμίου Πολέμου, όταν οι στρατιωτικές ανάγκες απαιτούσαν αξιόπιστα μέσα πλοήγησης. Το πρώτο σύστημα που αναπτύχθηκε ήταν το CONSOL, το οποίο χρησιμοποιήθηκε κυρίως από τα γερμανικά υποβρύχια. Το CONSOL βασιζόταν στη χρήση ισοδιάστατων καμπυλών για την παροχή πληροφοριών πλοήγησης σε μεγάλες αποστάσεις.
Το σύστημα DECCA, που αναπτύχθηκε από τους Βρετανούς, χρησιμοποιήθηκε ευρέως κατά την απόβαση της Νορμανδίας το 1944. Το DECCA προσέφερε υψηλή ακρίβεια σε περιορισμένες περιοχές και ήταν ιδιαίτερα χρήσιμο για τις επιχειρήσεις προσέγγισης ακτών. Μετά τον πόλεμο, το DECCA υιοθετήθηκε και για εμπορική χρήση, κυρίως στην Ευρώπη.
Το LORAN (Long Range Navigation) αναπτύχθηκε από τις Ηνωμένες Πολιτείες το 1940. Το αρχικό σύστημα LORAN-A λειτουργούσε σε υψηλότερες συχνότητες και είχε περιορισμένη ακρίβεια. Το 1957, το LORAN-C αντικατέστησε το LORAN-A, προσφέροντας μεγαλύτερη εμβέλεια και ακρίβεια, καθώς και ανθεκτικότητα στις παρεμβολές. Το LORAN-C έγινε το βασικό σύστημα υπερβολικής ναυτιλίας για τις Ηνωμένες Πολιτείες και πολλές άλλες χώρες.
Σήμερα, αν και η χρήση των συστημάτων αυτών έχει μειωθεί λόγω της ευρείας υιοθέτησης του GPS, το LORAN-C και το eLORAN (η εξέλιξή του) εξακολουθούν να χρησιμοποιούνται ως εφεδρικά συστήματα. Το eLORAN προσφέρει βελτιωμένη ακρίβεια και δυνατότητες, όπως η ενσωμάτωση δεδομένων μέσω διαδικτύου, καθιστώντας το ιδανικό για περιοχές χωρίς δορυφορική κάλυψη.
Εξέλιξη του LORAN-C και μεταβατικές τεχνολογίες
Η εξέλιξη του LORAN-C καθιστά το σύστημα ακόμα πιο αξιόπιστο και λειτουργικό για τις σύγχρονες ανάγκες της ναυτιλίας και άλλων βιομηχανιών. Αν και οι σύγχρονες τεχνολογίες πλοήγησης, όπως το GPS, έχουν μειώσει την εξάρτηση από το LORAN-C, το σύστημα εξακολουθεί να παίζει σημαντικό ρόλο στην παροχή αξιόπιστης πλοήγησης, ιδιαίτερα σε περιοχές όπου οι δορυφορικές υπηρεσίες δεν είναι επαρκώς διαθέσιμες.
Τα τελευταία χρόνια, αναπτύχθηκε το σύστημα eLORAN (Enhanced LORAN), το οποίο συνδυάζει τα πλεονεκτήματα του παραδοσιακού LORAN-C με σύγχρονες τεχνολογίες και παρέχει ακόμη μεγαλύτερη ακρίβεια και σταθερότητα, καθώς και δυνατότητες για την ενσωμάτωση άλλων τεχνολογιών, όπως το GPS, για αυξημένη αξιοπιστία και ακριβή γεωεντοπισμό.
Η ανάπτυξη του eLORAN προσφέρει μεγαλύτερη αντοχή στις ηλεκτρομαγνητικές παρεμβολές, επιτρέποντας τη συνεχιζόμενη χρήση του LORAN σε περιοχές που υπόκεινται σε διαταραχές λόγω υπερφόρτωσης δορυφορικών συστημάτων ή άλλων τεχνολογικών προκλήσεων. Επίσης, το eLORAN παρέχει τη δυνατότητα για μεγαλύτερη ευελιξία και ακριβέστερη παρακολούθηση σε περιβάλλοντα υψηλής απαιτητικότητας, όπως οι ακραίες καιρικές συνθήκες ή τα περιβάλλοντα με έντονες μαγνητικές παρεμβολές.
Η εξέλιξη αυτών των τεχνολογιών διασφαλίζει ότι το LORAN-C και τα μελλοντικά συστήματα πλοήγησης μπορούν να παραμείνουν μια πολύτιμη εφεδρική και βοηθητική λύση στην παγκόσμια ναυτιλία και άλλες βιομηχανίες, ακόμη και στην εποχή των δορυφορικών συστημάτων πλοήγησης.
Η συνεχής πρόοδος και αναβάθμιση του LORAN-C, καθώς και η ανάπτυξη του συστήματος eLORAN, έχει φέρει σημαντικές βελτιώσεις στην ακρίβεια και την αξιοπιστία των συστημάτων πλοήγησης. Με το eLORAN, το παραδοσιακό σύστημα LORAN έχει επαναστατήσει για να καλύψει τις σύγχρονες ανάγκες σε διάφορους τομείς, εξασφαλίζοντας υψηλότερη ακρίβεια και καλύτερη απόδοση σε περιβάλλοντα που προηγουμένως είχαν δυσκολίες λόγω της έλλειψης αξιόπιστης δορυφορικής κάλυψης ή λόγω των περιορισμών που θέτουν φυσικά εμπόδια, όπως τα βουνά ή οι αστικές περιοχές με πολλές παρεμβολές.
6.1. Αναβάθμιση και ενοποίηση με GPS και άλλες τεχνολογίες
Η ανάπτυξη του eLORAN δεν περιορίζεται μόνο στη βελτίωση της ακρίβειας του σήματος, αλλά και στην ενοποίηση του με άλλα σύγχρονα συστήματα πλοήγησης, όπως το GPS, οι δορυφορικές επικοινωνίες και οι αισθητήρες υψηλής ακρίβειας. Η ενοποίηση αυτών των τεχνολογιών παρέχει μια υπερσύγχρονη λύση για πλοήγηση σε πραγματικό χρόνο, εξασφαλίζοντας πολλαπλές γραμμές ασφάλειας και εφεδρικά συστήματα για τον εντοπισμό σφαλμάτων ή τη διαχείριση παραμέτρων.
Το eLORAN έχει τη δυνατότητα να ενσωματώνει δεδομένα από συστήματα όπως το GPS ή το GALILEO, και να προσφέρει ταυτόχρονα αυξημένη ακρίβεια στον προσδιορισμό θέσης (με περιθώριο σφάλματος μερικών μέτρων) σε σχέση με το παραδοσιακό LORAN-C. Αυτή η δυνατότητα δημιουργεί ένα πολύ ισχυρό και αξιόπιστο σύστημα για εφαρμογές υψηλής ακρίβειας, όπως στην παρακολούθηση της ναυσιπλοΐας, στην επιστημονική έρευνα ή στις υπεράκτιες βιομηχανίες, όπου η ακρίβεια και η αδιάλειπτη λειτουργία είναι κρίσιμης σημασίας.
6.2. Αντοχή στις Παρεμβολές και Διαταραχές
Το LORAN-C, και κατ' επέκταση το eLORAN, είναι ιδιαίτερα ανθεκτικό στις παρεμβολές που μπορεί να επηρεάσουν τα δορυφορικά συστήματα, όπως το GPS. Ένα από τα μεγαλύτερα πλεονεκτήματα του LORAN-C είναι η ικανότητά του να λειτουργεί ανεξάρτητα από τις συνθήκες του καιρού ή από τις μαγνητικές και ηλεκτρομαγνητικές παρεμβολές που μπορεί να προκύψουν σε περιοχές με πυκνές ηλεκτρονικές συσκευές, όπως οι αστικές περιοχές ή οι περιοχές κοντά σε στρατηγικές εγκαταστάσεις. Το eLORAN, ενσωματώνοντας εξελιγμένες τεχνολογίες για την ανίχνευση και αποτροπή παρεμβολών, διασφαλίζει την αξιόπιστη λειτουργία του, ακόμα και σε δύσκολες ή επικίνδυνες περιοχές.
Αυτή η ανθεκτικότητα είναι επίσης χρήσιμη σε εφαρμογές όπως η ναυτιλία, όπου τα πλοία βρίσκονται σε ανοιχτές θάλασσες ή σε περιοχές με πυκνές καταιγίδες και περιορισμένη ορατότητα. Επιπλέον, η αξιοπιστία του eLORAN το καθιστά ιδανικό για χρήση σε απομακρυσμένες περιοχές, όπως υπεράκτιες πλατφόρμες πετρελαίου, υπόγειες ή υποθαλάσσιες γεωτρήσεις, καθώς και για άλλες βιομηχανίες που απαιτούν αξιόπιστη πλοήγηση σε περιβάλλοντα με υψηλά επίπεδα θορύβου και διαταραχών.
6.3. Μακροπρόθεσμη Βιωσιμότητα και Κόστος
Ένα άλλο σημαντικό πλεονέκτημα του eLORAN είναι το χαμηλότερο κόστος λειτουργίας σε σχέση με τα δορυφορικά συστήματα. Η υποδομή του eLORAN απαιτεί μικρότερο κόστος συντήρησης και εγκατάστασης σε σχέση με τα σύγχρονα συστήματα GPS ή άλλες δορυφορικές υπηρεσίες. Ειδικά για εφαρμογές σε περιοχές όπου το GPS δεν είναι επαρκές ή δεν είναι διαθέσιμο, η εφαρμογή του LORAN-C ή του eLORAN μπορεί να αποδειχθεί πιο οικονομική και ευέλικτη επιλογή.
Για παράδειγμα, σε θαλάσσιες περιοχές όπου η εμβέλεια των δορυφορικών συστημάτων μπορεί να είναι περιορισμένη λόγω γεωγραφικών χαρακτηριστικών (όπως σε στενά, απομονωμένα ή παγωμένα ύδατα), το LORAN-C και το eLORAN προσφέρουν μια πιο βιώσιμη λύση για την παροχή αξιόπιστης πλοήγησης χωρίς το υψηλό κόστος των δορυφορικών συστημάτων.
6.4. Μέλλον του eLORAN και Συνεχιζόμενη Ανάπτυξη
Η συνεχιζόμενη ανάπτυξη του eLORAN επικεντρώνεται στη βελτίωση της ακρίβειας και της συμβατότητας με άλλες τεχνολογίες πλοήγησης, όπως το GNSS (Global Navigation Satellite System) και το INS (Inertial Navigation System). Αυτό θα επιτρέψει την εφαρμογή του eLORAN σε ένα ευρύτερο φάσμα εφαρμογών, όχι μόνο στην ναυτιλία αλλά και σε άλλες βιομηχανίες, όπως η γεωργία ακριβείας, η αεροπορία, και η επιστημονική έρευνα.
Μια από τις πιο σημαντικές μελλοντικές κατευθύνσεις για το eLORAN είναι η ενσωμάτωσή του σε μια πλήρως ενοποιημένη λύση γεωχωρικής πλοήγησης. Αυτή η ενσωμάτωση θα εξασφαλίσει ότι η σύγχρονη πλοήγηση θα βασίζεται σε ένα δίκτυο πολλών διαφορετικών συστημάτων, εξασφαλίζοντας μεγαλύτερη ακρίβεια και αξιόπιστη λειτουργία, ακόμη και σε απομακρυσμένα ή επικίνδυνα περιβάλλοντα.
Η ανάπτυξη του eLORAN αποτελεί μια ισχυρή ένδειξη του ότι, παρά την επικράτηση των δορυφορικών συστημάτων πλοήγησης, οι παραδοσιακές τεχνολογίες όπως το LORAN-C μπορούν να προσαρμοστούν και να αναβαθμιστούν για να καλύψουν τις ανάγκες της σύγχρονης ναυτιλίας και άλλων βιομηχανιών, συνεχίζοντας να παρέχουν αξιόπιστες λύσεις πλοήγησης και γεωεντοπισμού.
6.5. Επιπτώσεις του eLORAN στην Ασφάλεια της Ναυσιπλοΐας
Η εισαγωγή και εξέλιξη του eLORAN αναμένεται να έχει καθοριστική επίδραση στην ασφάλεια της ναυσιπλοΐας. Η ακριβής και αξιόπιστη πλοήγηση είναι ζωτικής σημασίας για την αποφυγή ατυχημάτων και για την ασφαλή μετακίνηση των πλοίων, ειδικά σε περιοχές με περιορισμένη κάλυψη δορυφορικών συστημάτων ή σε δύσκολες καιρικές συνθήκες. Το eLORAN, με την ικανότητά του να παρέχει συνεχή και ακριβή σήματα σε αντίξοες συνθήκες, μπορεί να λειτουργήσει ως κρίσιμο εργαλείο για τη βελτίωση της ασφάλειας των πλοίων.
Ειδικά σε περιοχές όπου τα σήματα GPS ενδέχεται να μην είναι διαθέσιμα ή να υποφέρουν από σφάλματα λόγω παρεμβολών, το eLORAN θα διασφαλίσει ότι οι ναυτικοί και οι πλοίαρχοι μπορούν να βασίζονται σε μια δεύτερη, αξιόπιστη πηγή πλοήγησης. Το γεγονός ότι το eLORAN μπορεί να προσφέρει ακριβή δεδομένα θέσης ακόμα και σε περιοχές με υψηλές παρεμβολές, όπως περιοχές με ισχυρές ηλεκτρομαγνητικές διαταραχές, καθιστά το σύστημα ένα απαραίτητο εργαλείο για την αποφυγή ναυτικών ατυχημάτων και την ενίσχυση της συνολικής ασφάλειας του ναυτικού στόλου.
6.6. Κανονιστικές Προεκτάσεις και Υιοθέτηση από Διεθνείς Οργανισμούς
Η επιτυχής ανάπτυξη και εφαρμογή του eLORAN αναμένεται να επηρεάσει τις διεθνείς κανονιστικές πολιτικές για την πλοήγηση και την ασφάλεια της ναυσιπλοΐας. Ο Διεθνής Ναυτιλιακός Οργανισμός (IMO) και άλλοι κανονιστικοί φορείς ενδέχεται να ενσωματώσουν το eLORAN στα διεθνή πρότυπα πλοήγησης, καθιστώντας το υποχρεωτικό για την εφαρμογή σε νέες ναυτιλιακές μονάδες ή για την αναβάθμιση των υφιστάμενων πλοίων.
Με την αυξανόμενη εξάρτηση από δορυφορικά συστήματα πλοήγησης, πολλές ναυτιλιακές εταιρείες και χώρες αναγνωρίζουν την ανάγκη για εφεδρικά συστήματα που να μπορούν να διασφαλίσουν την αδιάλειπτη πλοήγηση, ακόμα και σε περιπτώσεις που το GPS ή άλλα συστήματα GNSS παρουσιάζουν προβλήματα ή σφάλματα. Ως αποτέλεσμα, η ενσωμάτωσή του eLORAN ως εφεδρικό σύστημα πλοήγησης μπορεί να συμβάλλει στη δημιουργία πιο αυστηρών και αξιόπιστων διεθνών κανονισμών για την ασφάλεια των θαλάσσιων μεταφορών.
6.7. Ανάγκη για Εκπαίδευση και Υποστήριξη
Η επιτυχία της εφαρμογής του eLORAN εξαρτάται επίσης από τη σωστή εκπαίδευση των ναυτικών και των επαγγελματιών του τομέα. Η κατανόηση των δυνατοτήτων και των περιορισμών του συστήματος είναι ζωτικής σημασίας για την αποδοτική και ασφαλή χρήση του στην καθημερινή ναυτιλιακή πρακτική. Οι ναυτικοί, οι πλοίαρχοι και οι υπεύθυνοι για τη ναυσιπλοΐα θα πρέπει να εκπαιδευτούν στις τεχνικές λειτουργίες του eLORAN, καθώς και στους τρόπους ενσωμάτωσής του με άλλα συστήματα πλοήγησης και επικοινωνίας.
Πέρα από την εκπαίδευση, θα είναι σημαντικό οι ναυτιλιακές εταιρείες και οι φορείς που διαχειρίζονται το δίκτυο eLORAN να παρέχουν την απαραίτητη τεχνική υποστήριξη και συντήρηση των συστημάτων. Αυτό θα εξασφαλίσει τη συνεχιζόμενη αξιοπιστία και αποτελεσματικότητα του eLORAN σε διάφορες περιβάλλοντα, συμπεριλαμβανομένων των ακραίων καιρικών φαινομένων και των περιοχών με πυκνές παρεμβολές.
6.8. Συμπεράσματα
Η αναβάθμιση του παραδοσιακού συστήματος LORAN-C σε eLORAN έχει θέσει τις βάσεις για μια νέα εποχή στην ναυσιπλοΐα και στις τεχνολογίες γεωεντοπισμού. Με την αυξημένη ακρίβεια, την ανθεκτικότητα σε παρεμβολές και το χαμηλότερο κόστος λειτουργίας, το eLORAN προσφέρει μια εξαιρετική εναλλακτική λύση στα υπάρχοντα συστήματα πλοήγησης, όπως το GPS, και ενισχύει την ασφάλεια και την αξιοπιστία των ναυτικών δραστηριοτήτων.
Η μελλοντική επιτυχία του eLORAN θα εξαρτηθεί από την περαιτέρω ανάπτυξή του, τη συνεργασία μεταξύ διεθνών οργανισμών και κρατών, καθώς και από τη συνεχιζόμενη εκπαίδευση και υποστήριξη των χρηστών. Το eLORAN, σε συνδυασμό με άλλες τεχνολογίες πλοήγησης, θα αποτελέσει έναν ακρογωνιαίο λίθο για την ασφαλή και αποδοτική ναυσιπλοΐα στον 21ο αιώνα.
6.9. Προκλήσεις και Μελλοντικές Προοπτικές του eLORAN
Παρά τα προφανή πλεονεκτήματα του eLORAN, η υιοθέτησή του δεν έρχεται χωρίς προκλήσεις. Μια από τις κύριες δυσκολίες που αντιμετωπίζει το σύστημα είναι η ανάγκη για εκτεταμένη υποδομή και επενδύσεις. Αν και το eLORAN έχει το πλεονέκτημα της υψηλής ακρίβειας και ανθεκτικότητας, η κατασκευή και η συντήρηση του δικτύου σταθμών εκπομπής απαιτεί σημαντικούς πόρους και χρόνος. Οι ναυτιλιακές εταιρείες και οι κυβερνήσεις θα πρέπει να διασφαλίσουν ότι η υποδομή αυτή θα είναι σε θέση να υποστηρίξει την παγκόσμια ναυτιλιακή βιομηχανία, παρέχοντας παράλληλα την απαιτούμενη υποστήριξη για τη συνεχιζόμενη λειτουργία του δικτύου.
Μια άλλη πρόκληση είναι η ενσωμάτωση του eLORAN σε υπάρχοντα συστήματα πλοήγησης. Η συνεργασία μεταξύ διαφορετικών τεχνολογιών και η εξασφάλιση της αλληλεπίδρασης τους χωρίς να προκαλούνται προβλήματα από παρεμβολές ή αναντιστοιχίες στις πληροφορίες μπορεί να αποδειχθεί περίπλοκο έργο. Η ανάγκη για συντονισμένα πρότυπα και τη δημιουργία διαλειτουργικότητας με άλλες πλοηγητικές και επικοινωνιακές πλατφόρμες είναι ζωτικής σημασίας για την επιτυχία του eLORAN στον πραγματικό κόσμο.
Ωστόσο, παρά τις προκλήσεις, οι προοπτικές για το μέλλον του eLORAN είναι αισιόδοξες. Η ενσωμάτωσή του στην παγκόσμια ναυτιλιακή βιομηχανία μπορεί να συμβάλει στην αυξημένη ασφάλεια και αποτελεσματικότητα των θαλάσσιων μεταφορών. Επιπλέον, η τεχνολογική εξέλιξη και οι επενδύσεις στην υποδομή του συστήματος αναμένεται να μειώσουν το κόστος και να ενισχύσουν τη διαθεσιμότητα του eLORAN σε όλο τον κόσμο.
6.10. Πολιτική Υποστήριξη και Διεθνής Συνεργασία
Η αποτελεσματική ανάπτυξη και εφαρμογή του eLORAN εξαρτάται από την ισχυρή πολιτική υποστήριξη και τη διεθνή συνεργασία. Οι κυβερνήσεις και οι διεθνείς οργανισμοί πρέπει να κατανοήσουν την ανάγκη για δημιουργία ενός εφεδρικού συστήματος πλοήγησης που να λειτουργεί σε συνδυασμό με τα υπάρχοντα συστήματα GNSS. Η συνεργασία μεταξύ κρατών, φορέων ανάπτυξης τεχνολογίας, και των διεθνών οργανισμών όπως ο Διεθνής Ναυτιλιακός Οργανισμός (IMO) και η Διεθνής Ένωση Τηλεπικοινωνιών (ITU) είναι κρίσιμη για τη δημιουργία ενιαίων προτύπων και κανονισμών που θα εξασφαλίσουν την επιτυχή υιοθέτηση του eLORAN σε παγκόσμιο επίπεδο.
Η πολιτική υποστήριξη είναι επίσης σημαντική για την εξασφάλιση της χρηματοδότησης για τη δημιουργία και τη συντήρηση της απαιτούμενης υποδομής eLORAN. Η ενσωμάτωσή του σε κανονιστικά πλαίσια θα ενισχύσει τη διαλειτουργικότητα και την αξιοπιστία του συστήματος, καθιστώντας το ένα βασικό εργαλείο για την ασφαλή ναυσιπλοΐα του μέλλοντος.
6.11. Συνοψίζοντας τις Ανάγκες του Μέλλοντος
Το μέλλον του eLORAN φαίνεται να είναι γεμάτο προοπτικές, ωστόσο οι ναυτιλιακές εταιρείες, οι κυβερνήσεις και οι διεθνείς οργανισμοί θα πρέπει να συνεχίσουν να επενδύουν στη βελτίωση του συστήματος και στη διάδοση της τεχνολογίας αυτής. Η ανάπτυξη σύγχρονων υποδομών, η ενσωμάτωσή του σε υπάρχοντα συστήματα και η ενίσχυση της εκπαίδευσης των ναυτικών θα αποτελέσουν βασικά σημεία για την επιτυχή εφαρμογή του eLORAN στην παγκόσμια ναυτιλία.
Εν κατακλείδι, το eLORAN υπόσχεται να γίνει το νέο πρότυπο στη ναυτιλία για την αξιόπιστη και ασφαλή πλοήγηση, και με τη σωστή υποστήριξη και συνεργασία σε διεθνές επίπεδο, μπορεί να επιφέρει θετικές αλλαγές στην ασφάλεια και την αποδοτικότητα των θαλάσσιων μεταφορών.
Ενδεχομένως να υπάρχουν κάποιες επιπλέον πτυχές που μπορούν να αναλυθούν, ειδικά όσον αφορά τις μελλοντικές εφαρμογές του eLORAN ή άλλων συστημάτων υπερβολικής ναυτιλίας, καθώς και τις νέες τάσεις στην ανάπτυξη της ναυτιλίας, όπως τα "έξυπνα" πλοία και η αυτόνομη ναυσιπλοΐα.
6.12. Η Συμβολή της Τεχνολογίας στο Μέλλον της Ναυτιλίας
Η εξέλιξη των τεχνολογιών, όπως η Τεχνητή Νοημοσύνη (AI) και το Διαδίκτυο των Πραγμάτων (IoT), αναμένεται να φέρει ριζικές αλλαγές στον τρόπο που οι ναυτιλιακές εταιρείες χρησιμοποιούν τα συστήματα πλοήγησης. Ο συνδυασμός αυτών των τεχνολογιών με το eLORAN ή άλλες μορφές υπερβολικής ναυτιλίας μπορεί να οδηγήσει στην ανάπτυξη "έξυπνων" πλοίων που θα είναι σε θέση να λαμβάνουν αυτόματα αποφάσεις για την πορεία τους, την αποφυγή κινδύνων και τη βελτίωση της αποδοτικότητας των διαδρομών. Το eLORAN μπορεί να λειτουργήσει ως βασικό σύστημα εφεδρείας για την πλοήγηση αυτών των πλοίων σε περιοχές με περιορισμένη δορυφορική κάλυψη ή κατά τη διάρκεια παρεμβολών.
6.13. Ανάγκες για Εκπαίδευση και Κατάρτιση
Η ανάπτυξη και υιοθέτηση του eLORAN απαιτεί επίσης επένδυση στην εκπαίδευση και την κατάρτιση των ναυτικών, καθώς και των τεχνικών που αναλαμβάνουν τη συντήρηση του συστήματος. Η σωστή εκπαίδευση των χειριστών για τη χρήση και την αξιοποίηση του συστήματος, καθώς και η αναγνώριση και διόρθωση σφαλμάτων, θα διασφαλίσουν τη συνεχιζόμενη λειτουργικότητα και αξιοπιστία του. Οι ναυτικοί θα πρέπει να είναι σε θέση να αντιλαμβάνονται την πραγματική αξία και τις δυνατότητες του eLORAN σε διάφορες συνθήκες, ενώ παράλληλα να κατανοούν τις περιορισμένες καταστάσεις που μπορεί να αντιμετωπίσουν σε δύσκολες συνθήκες.
6.14. Υποστήριξη και Συντήρηση Υποδομών
Η συντήρηση και η αναβάθμιση της υποδομής του eLORAN είναι επίσης ένας τομέας που απαιτεί συνεχιζόμενη υποστήριξη. Αυτό περιλαμβάνει την τακτική αναβάθμιση των σταθμών εκπομπής, τη διασφάλιση της ποιότητας των σημάτων και την ενσωμάτωση νέων τεχνολογιών για την αύξηση της ακρίβειας και της αποτελεσματικότητας του συστήματος. Επίσης, απαιτείται συνεχής παρακολούθηση και αξιολόγηση της απόδοσης του συστήματος σε πραγματικές συνθήκες, για να διασφαλιστεί ότι ανταποκρίνεται στις σύγχρονες απαιτήσεις της ναυτιλιακής βιομηχανίας.
Με αυτά τα σημεία, μπορούμε να διαπιστώσουμε ότι το eLORAN, παρόλο που έχει περιορισμένη χρήση σε σύγκριση με το GPS, παραμένει ένα αξιόπιστο και χρήσιμο εργαλείο στον τομέα της ναυσιπλοΐας, με σημαντική συμβολή στην αύξηση της ασφάλειας και της αποδοτικότητας των θαλάσσιων μεταφορών, ειδικά σε περιοχές με περιορισμένη ή καθόλου δορυφορική κάλυψη.
++++++++++++++++++++++
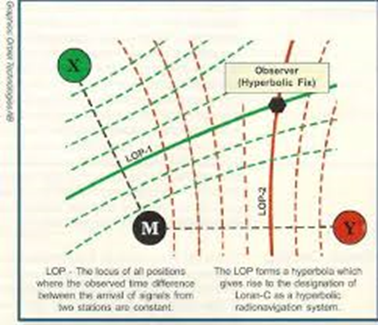
Ανάλυση Φωτογραφίας 1: Διάγραμμα Υπερβολικών Καμπυλών
Η πρώτη φωτογραφία παρουσιάζει ένα διάγραμμα που απεικονίζει τις βασικές αρχές λειτουργίας του συστήματος LORAN-C (Long Range Navigation). Το σύστημα LORAN-C είναι ένα χερσαίο ραδιοναυτιλιακό σύστημα που χρησιμοποιεί τη διαφορά χρόνου λήψης ραδιοσημάτων από δύο ή περισσότερους σταθμούς για να προσδιορίσει τη θέση του δέκτη.
Βασικές Αρχές
Το διάγραμμα περιλαμβάνει υπερβολικές καμπύλες, οι οποίες αντιστοιχούν στις Γραμμές Θέσης (Lines of Position – LOP). Οι καμπύλες αυτές είναι τοποθεσίες όπου η διαφορά του χρόνου άφιξης ραδιοσημάτων από δύο σταθμούς είναι σταθερή. Με άλλα λόγια, κάθε καμπύλη αντιπροσωπεύει μια συγκεκριμένη διαφορά χρόνου ανάμεσα σε δύο σταθμούς εκπομπής.
Σημεία Αναφοράς:
1. Σταθμοί X και Y:
o Οι δύο σταθμοί εκπέμπουν σήματα που συγχρονίζονται χρονικά.
o Τα σήματα αυτά ταξιδεύουν μέσω της ατμόσφαιρας και φτάνουν στον δέκτη με διαφορετικούς χρόνους άφιξης λόγω της απόστασης.
2. Σταθμός M:
o Ο σταθμός M χρησιμεύει ως κύριος σταθμός (Master Station) που συγχρονίζεται με τους άλλους δύο.
3. Παρατηρητής (Observer):
o Το σημείο όπου τέμνονται δύο υπερβολικές καμπύλες αντιπροσωπεύει τη θέση του παρατηρητή ή του δέκτη.
o Ο παρατηρητής χρησιμοποιεί τη διαφορά χρόνου για να προσδιορίσει τη θέση του πάνω στον χάρτη.
Η Υπερβολική Πλοήγηση
Η βασική αρχή της υπερβολικής πλοήγησης βασίζεται στην εξίσωση υπερβολής:
|dx-dy|=k,
όπου:
- dx και dy: Οι αποστάσεις από τον δέκτη προς τους σταθμούς X και Y, αντίστοιχα.
- k: Η διαφορά των αποστάσεων, η οποία αντιστοιχεί στη διαφορά χρόνου άφιξης των σημάτων (Δt) πολλαπλασιασμένη με την ταχύτητα διάδοσης του σήματος.
Αυτή η εξίσωση περιγράφει μια υπερβολική καμπύλη, δηλαδή ένα γεωμετρικό τόπο σημείων όπου η διαφορά των αποστάσεων από δύο σταθερά σημεία (σταθμούς εκπομπής X και Y) παραμένει σταθερή.
Η καμπύλη αυτή είναι το κλειδί για τον προσδιορισμό της θέσης του δέκτη. Συνδυάζοντας δύο ή περισσότερες υπερβολικές καμπύλες από διαφορετικά ζεύγη σταθμών, μπορεί να βρεθεί το σημείο τομής τους, που αντιστοιχεί στη θέση του παρατηρητή ή του δέκτη.
Επεξήγηση
Το σύστημα LORAN-C εκμεταλλεύεται αυτή τη γεωμετρική αρχή, χρησιμοποιώντας συγχρονισμένα ραδιοσήματα για τη μέτρηση της χρονικής διαφοράς λήψης (Δt). Οι σταθμοί εκπομπής είναι εξοπλισμένοι με ακριβή ρολόγια για να διασφαλιστεί η ακρίβεια στον συγχρονισμό των σημάτων.
Με αυτό τον τρόπο, το LORAN-C προσφέρει έναν αξιόπιστο μηχανισμό για την πλοήγηση, ακόμα και σε αποστάσεις εκατοντάδων χιλιομέτρων.
Εφαρμογές
Το LORAN-C χρησιμοποιείται κυρίως στη ναυτιλία και την αεροπλοΐα για:
1. Ακρίβεια Πλοήγησης: Παρέχει ακριβείς συντεταγμένες στον χάρτη.
2. Ασφάλεια: Βοηθά τα πλοία να αποφύγουν κινδύνους, όπως ύφαλους και στενά περάσματα.
3. Πλοήγηση Μεγάλης Ακτίνας: Λειτουργεί σε αποστάσεις εκατοντάδων χιλιομέτρων, καθιστώντας το ιδανικό για υπερπόντιες διαδρομές.
Τεχνικές Λεπτομέρειες
- Το LORAN-C λειτουργεί στη ζώνη συχνοτήτων LF (Low Frequency), περίπου στα 100 kHz.
- Η χρονική ακρίβεια των σημάτων επιτυγχάνεται μέσω εξαιρετικά συγχρονισμένων ρολογιών στους σταθμούς εκπομπής.
- Ο δέκτης χρησιμοποιεί πολύπλοκους αλγόριθμους για να μετατρέψει τις διαφορές χρόνου σε γεωγραφικές συντεταγμένες.
Περιορισμοί
- Ποιότητα Σήματος: Η ποιότητα μπορεί να επηρεαστεί από τις ατμοσφαιρικές συνθήκες.
- Απαιτούμενος Εξοπλισμός: Απαιτούνται εξειδικευμένοι δέκτες για την ερμηνεία των σημάτων.
Το συγκεκριμένο διάγραμμα παρέχει μια σαφή οπτική αναπαράσταση της υπερβολικής πλοήγησης, διευκολύνοντας την κατανόηση της λειτουργίας του LORAN-C.
Ανάλυση Φωτογραφίας 2: Συσκευή Δέκτη LORAN-C
Η δεύτερη φωτογραφία παρουσιάζει έναν δέκτη LORAN-C, ο οποίος χρησιμοποιείται στη ναυτιλία και την αεροπλοΐα για τον προσδιορισμό θέσης.
Περιγραφή της Συσκευής
Ο δέκτης της φωτογραφίας φέρει την ένδειξη “KODEN” και διαθέτει:
1. Οθόνες: Ψηφιακές οθόνες που εμφανίζουν δεδομένα πλοήγησης, όπως γεωγραφικές συντεταγμένες (γεωγραφικό πλάτος και μήκος).
2. Πληκτρολόγιο Εισαγωγής: Ένα αριθμητικό πληκτρολόγιο για την εισαγωγή δεδομένων, όπως συντεταγμένες προορισμού.
3. Διακόπτες και Κουμπιά: Χρησιμοποιούνται για την εναλλαγή λειτουργιών, τη ρύθμιση και τη βαθμονόμηση του δέκτη.
4. Στερέωση: Ο δέκτης είναι τοποθετημένος σε βάση για σταθερότητα.
Λειτουργία
Ο δέκτης λειτουργεί ως εξής:
1. Λήψη Σημάτων: Λαμβάνει ραδιοσήματα από σταθμούς LORAN-C.
2. Επεξεργασία Σημάτων: Υπολογίζει τις διαφορές χρόνου άφιξης των σημάτων.
3. Υπολογισμός Θέσης: Μετατρέπει τις χρονικές διαφορές σε γεωγραφικές συντεταγμένες μέσω υπερβολικών καμπυλών.
4. Εμφάνιση Δεδομένων: Παρουσιάζει τις συντεταγμένες και άλλες πληροφορίες πλοήγησης στις οθόνες.
Χρήσεις
Οι δέκτες LORAN-C χρησιμοποιούνται ευρέως για:
1. Ναυτιλία: Βοηθούν τα πλοία να προσδιορίσουν τη θέση τους στη θάλασσα.
2. Αεροπλοΐα: Χρησιμοποιούνται για την πλοήγηση αεροσκαφών, ειδικά σε περιοχές με ελάχιστη κάλυψη GPS.
3. Έρευνα και Διάσωση: Παρέχουν ακριβείς συντεταγμένες για την καθοδήγηση ομάδων διάσωσης.
Πλεονεκτήματα του LORAN-C
- Υψηλή Ακρίβεια: Παρέχει ακριβείς θέσεις, ιδιαίτερα σε περιοχές όπου το GPS είναι αναξιόπιστο.
- Ανθεκτικότητα: Λειτουργεί υπό δύσκολες καιρικές συνθήκες.
- Ασφάλεια: Παρέχει αξιόπιστα δεδομένα πλοήγησης, μειώνοντας τον κίνδυνο ατυχημάτων.
Τεχνικές Προδιαγραφές
Οι δέκτες LORAN-C, όπως αυτός της φωτογραφίας, είναι σχεδιασμένοι για:
1. Συμβατότητα με Συστήματα: Λειτουργούν με πολλούς σταθμούς εκπομπής.
2. Ευκολία Χρήσης: Εξοπλισμένοι με διαισθητικά χειριστήρια και ευανάγνωστες οθόνες.
3. Ανθεκτικότητα: Κατασκευασμένοι για να αντέχουν στις δύσκολες συνθήκες της θάλασσας και του αέρα.
Μειονεκτήματα
- Εξάρτηση από Υποδομή: Απαιτεί τη λειτουργία σταθμών LORAN-C.
- Περιορισμένη Εμβέλεια: Η ακρίβεια μειώνεται σε μεγάλες αποστάσεις από τους σταθμούς.
- Αντικατάσταση από GPS: Με την ευρεία υιοθέτηση του GPS, η χρήση του LORAN-C έχει περιοριστεί.
Ιστορική και Σύγχρονη Σημασία
Παρόλο που το GPS έχει αντικαταστήσει σε μεγάλο βαθμό το LORAN-C, το σύστημα παραμένει χρήσιμο ως εφεδρική μέθοδος πλοήγησης. Οι δέκτες όπως αυτός της φωτογραφίας συνεχίζουν να χρησιμοποιούνται σε ορισμένες περιοχές και εφαρμογές.
Συμπερασματικά, οι δύο φωογραφίες αναδεικνύουν τη θεωρητική και πρακτική διάσταση του συστήματος LORAN-C, παρουσιάζοντας τη διαδικασία υπερβολικής πλοήγησης και τον εξοπλισμό που χρησιμοποιείται για την εφαρμογή της.
Βιβλιογραφία
1. ΝΑΥΤΙΚΑ ΗΛΕΚΤΡΟΝΙΚΑ ΟΡΓΑΝΑ - ΠΑΛΛΗΚΑΡΗ – ΚΑΤΣΟΥΛΗ – ∆ΑΛΑΚΛΗ 2008, ΕΥΓΕΝΙΔΗΣ
2. ΤΑ ΌΡΓΑΝΑ ΤΗΣ ΓΕΦΥΡΑΣ ΣΤΑ ΣΥΓΧΡΟΝΑ ΕΜΠΟΡΙΚΑ ΠΛΟΙΑ – ΤΣΙΜΙΝΟΣ
3. ΝΑΥΤΙΚΑ ΗΛΕΚΤΡΟΝΙΚΑ ΟΡΓΑΝΑ ΙΙ – ΝΙΚΟΛΑΟΥ – ΣΗΜΕΙΩΣΕΙΣ Γ’ ΕΞΑΜΗΝΟΥ - 2009